In recent years, the Fintech industry has experienced exponential growth, revolutionizing the way financial services are delivered and consumed. From mobile banking and digital wallets to blockchain and peer-to-peer lending, Fintech innovations have made financial transactions more accessible, efficient, and secure.
However, with this rapid advancement comes the need for robust regulatory frameworks to ensure consumer protection, data privacy, and financial stability. This blog delves into Fintech regulation, exploring the various bodies responsible for oversight, the importance of regulation, and future trends in this dynamic sector.
Is Fintech regulated?
For many years, Fintech companies operated with minimal regulation, as regulatory bodies mainly concentrated on traditional banking institutions. However, as the Fintech sector has expanded, the regulatory framework has evolved accordingly.
Nowadays, Fintech firms in most countries are overseen by national financial regulators, with regulations increasingly customized to address the specific challenges and opportunities that Fintech presents. The global Fintech market is projected to reach a staggering $305 billion by 2025, highlighting the sector's rapid growth and significance.
Regulating the Fintech industry is inherently more complex than overseeing traditional financial institutions. Despite their smaller size, Fintech companies must adhere to stringent regulations aimed at ensuring consumer protection, data privacy, and financial stability. Furthermore, many Fintech firms operate across multiple jurisdictions from an early stage, requiring compliance with a wide range of regional and national regulations.

Why is regulation important for Fintechs?
Regulations have evolved to protect financial institutions, their customers, and the wider economy from financial crime. Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulation are frequently updated to reflect changes in fraudulent and criminal methods.
Wherever Fintechs operate – whether in financial services, customer verification, or transactions support – they should ensure the same checks and security as the major financial institutions.
Protection and compliance are vital – but there are other reasons For Fintechs to comply with regulation:
- Regulation establishes trust: Credibility and trust are vital for any financial-related company, and compliance with regulations helps to establish this.
- Regulation creates a level playing field: When companies operating in the same arena must meet the same requirements and challenges, this supports fair competition.
- Compliance helps Fintechs scale: This could include offering new products and services, moving to a full banking license, or expanding into new countries.
Who regulates Fintech companies?
Fintech companies operate in a regulated environment to ensure stability, security, and consumer protection. The regulatory landscape is complex and varies across jurisdictions. Various governmental and non-governmental bodies oversee Fintech firms to ensure compliance with financial regulations, consumer protection laws, and data privacy standards.
This section will explore the key regulatory bodies in major regions, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Europe, and other parts of the world, highlighting their roles and responsibilities in regulating the Fintech industry.
Regulatory bodies in the US
Fintech companies are regulated by a variety of governmental and non-governmental bodies, depending on the jurisdiction in which they operate. In the United States, several key agencies play a significant role in overseeing Fintech, below are some examples:
- The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB): Responsible for ensuring that consumers are treated fairly by financial institutions, including Fintech firms.
- The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC): Plays a crucial role by insuring deposits and examining financial institutions for safety, soundness, and consumer protection.
- The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC): Supervises national banks and federal savings associations, which can include Fintech companies that have obtained special-purpose national bank charters.
- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): Oversees Fintech firms involved in securities trading and investment activities, ensuring compliance with securities laws.
- The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN): A critical body, focusing on anti-money laundering (AML) and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT) regulations.
Regulatory Bodies in the UK
In the United Kingdom, the primary regulatory bodies overseeing Fintech companies are:
- Financial Conduct Authority (FCA): Ensures that Fintech firms comply with financial regulations and consumer protection laws.
- Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA): Works alongside the FCA to supervise banks, building societies, and credit unions, which can include Fintech companies offering similar services.
Regulatory Bodies in Europe
In Europe, the regulatory landscape for Fintech companies is comprehensive and multi-faceted, involving several key authorities to ensure compliance and maintain financial stability. The primary regulatory bodies include:
- European Central Bank (ECB): Along with national regulatory authorities, the ECB ensures Fintech firms adhere to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other financial regulations.
- European Banking Authority (EBA): Sets regulatory standards and guidelines for Fintech companies in the EU, ensuring consistent prudential regulation and supervision across the banking sector.
- European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA): Plays a crucial role in overseeing securities markets and investment firms engaged in FinTech activities. Its regulatory framework aims to enhance investor protection and promote stable and orderly financial markets.
- European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA): Regulates the insurance and occupational pensions sectors, ensuring Fintech companies offering insurance-related financial products comply with regulatory standards to protect consumers and maintain market integrity.
- Individual member states have national regulatory bodies that work with EU authorities to regulate Fintech. For example, the Federal Financial Supervisory Authority (BaFin) in Germany collaborates with EU regulators to ensure compliance among Fintech firms.
Regulatory bodies in other regions
Across different regions and countries, various regulatory bodies exist, for example:
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF): Sets international standards for combating money laundering and terrorist financing, which Fintech companies must adhere to globally.
- Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS): Oversees Fintech activities and ensures compliance with local regulations in Singapore.
- Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA): Regulates Fintech operations and ensures adherence to local laws in Dubai and the broader Middle East region.
Licensing and registration
Requirements for Fintech's
Licensing and registration are crucial components of Fintech regulation, ensuring that companies adhere to the legal frameworks set by regulatory authorities. These processes are essential for maintaining the integrity of the financial system, safeguarding consumer interests, and fostering fair competition among Fintech firms.

Licensing and registration prerequisites for Fintech firms can differ widely. These differences are influenced by the jurisdiction, the nature of the financial services or products provided, and the business model. Typical requirements frequently encompass:
- Capital and financial resources: Fintech firms must show they have adequate capital and financial resources to ensure their operational viability and ability to fulfill compliance requirements.
- Governance and risk management frameworks: Strong governance structures, risk management procedures, and internal controls are typically necessary to ensure sound operations and effective oversight.
- Cybersecurity and data protection: Due to the tech-centric nature of Fintech, companies are required to implement robust cybersecurity measures and adhere to data protection laws to protect sensitive information.
- Anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) compliance: Fintech companies must establish effective AML and CTF programs to prevent their services from being exploited for illegal activities.
- “Fit and proper” test: Key individuals, such as directors and senior managers, must meet specific "fit and proper" standards, proving their integrity, competence, and experience.
Consumer Protection Laws
Ensuring the protection of consumers is paramount for Fintech companies. Regulatory bodies like the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the US have established consumer protection laws to promote transparency, prevent unfair or deceptive practices, and safeguard sensitive consumer information.
Fintech companies should adhere to the following regulations to operate ethically and treat consumers fairly:
- Disclosure and transparency: Fintech companies must offer clear, accurate, and comprehensive information about their products, services, fees, and terms and conditions. This enables consumers to make informed decisions.
- Data protection and privacy: Regulatory frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US set stringent rules for the collection, use, and protection of consumer data.
- Consent and control over data: Consumers should have control over their personal data. Fintech companies are required to obtain explicit consent for data collection and provide mechanisms for consumers to access, rectify, or delete their data as needed.
- Data minimization and retention policies: Fintech companies should only collect and retain the minimum amount of consumer data necessary for legitimate business purposes. They must securely dispose of or anonymize data that is no longer required.
- Complaint handling and dispute resolution mechanisms: Fintech companies must have robust processes in place to address consumer complaints and provide effective dispute resolution mechanisms. Consumers should be informed about how to recover their money if they are affected by a mistake or fraud.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance is a critical aspect of Fintech regulation, aimed at preventing the misuse of financial systems for illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing. Fintech companies, due to their digital nature and global reach, are particularly vulnerable to these risks. Therefore, adhering to AML regulations is not just a legal requirement but also a fundamental practice to ensure the integrity and trustworthiness of Fintech operations.
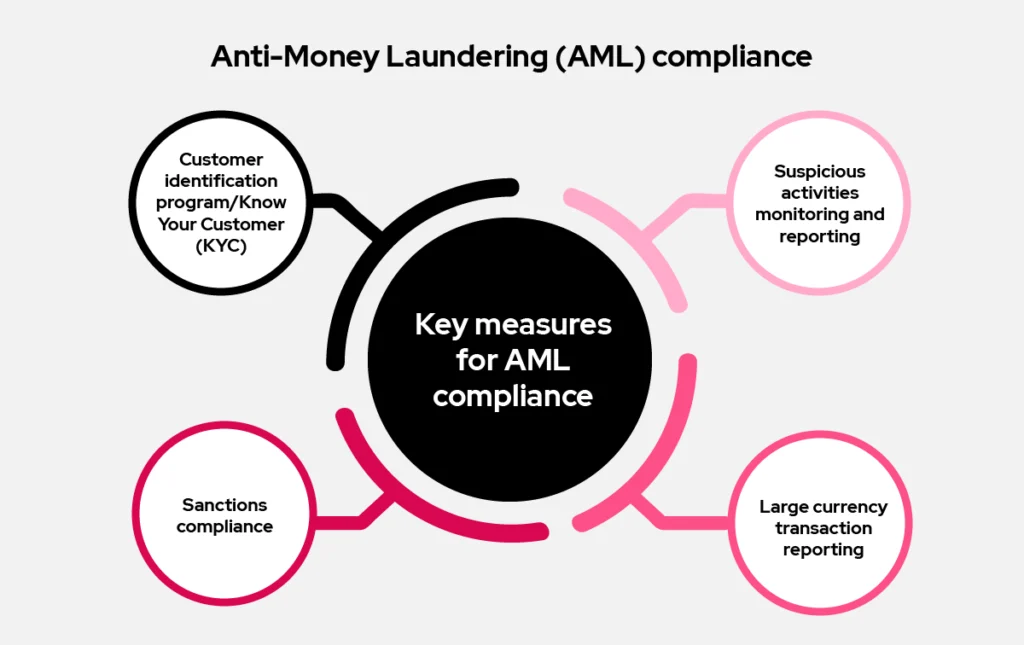
Key measures for AML compliance:
- Customer identification program/Know Your Customer (KYC): Fintech firms must verify customer identities to ensure legitimacy. Higher-risk services require more detailed documentation and scrutiny.
- Large currency transaction reporting: Institutions must file a Currency Transaction Report (CTR) for transactions above a certain threshold made by a single customer in a day. This helps track large sums of money that could be linked to money laundering.
- Suspicious activities monitoring and reporting: Regulatory agencies provide guidelines on behaviors to monitor, such as numerous cash deposits or withdrawals to avoid reporting thresholds. If suspicious behavior is detected, an investigator must file a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) or Suspicious Transaction Report (STR) with the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU).
- Sanctions compliance: Regulatory bodies require financial institutions to check transaction parties against lists of sanctioned individuals, companies, and countries. This ensures transactions do not involve sanctioned entities, reducing the risk of illegal activities.
By following these measures, Fintech firms can better detect and prevent suspicious activities, such as unusually large transactions, frequent transfers to high-risk areas, or transactions that do not match a customer's profile, which can trigger alerts for further investigation.
The future for Fintech regulation
As Fintech evolves, regulatory bodies are recognizing the need for more adaptable and flexible regulatory frameworks. Key trends include:
- Emergence of new technologies: As innovations like distributed ledger technology (DLT), central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), and decentralized finance (DeFi) become more common, regulators will need to create and adapt rules to manage the related risks and opportunities.
- Data privacy and cybersecurity: With the growing use of data and technology, ensuring data privacy and cybersecurity will remain a key focus for regulators, requiring strong protections and compliance measures.
- Digital identity solutions: Creating secure digital identity solutions will be essential for Fintech companies to meet Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations while improving customer experience.
- Financial inclusion: Regulators might aim to promote financial inclusion by supporting Fintech solutions that offer financial services to underserved communities and populations.
- Climate and ESG compliance: Regulatory authorities are likely to emphasize sustainable Fintech solutions and ensure adherence to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards.
- Customer education: Regulators may prioritize efforts to educate consumers about the risks and responsibilities of using FinTech products and services, promoting informed decision-making and consumer protection.
Conclusion
Fintech is revolutionizing the financial services industry, providing cutting-edge solutions that enhance convenience and accessibility. However, with significant innovation comes significant responsibility, necessitating regulatory oversight. Whether you run a Fintech startup or a large enterprise, staying informed, proactive, and adaptable in your compliance strategies is essential. Remain attuned to regulatory changes and utilize innovative methods to adhere to Fintech laws and regulations.